What is Industrial Design?
Industrial design is all about creating products that are not only practical but also look good. It involves designing things like products, systems, and services that meet the needs of users, can be made in factories, and are wanted by customers. Industrial designers think about stuff like how easy things are to use, how comfy they are to use, what they’re made of, how they’re made, and how sustainable they are, all to come up with smart and useful solutions.
This design field covers a whole bunch of products, including things people use every day like gadgets, furniture, home appliances, cars, and more. Industrial designers often work together with engineers, marketers, and other pros to turn ideas into real products. They use different tools and tricks like sketching, making prototypes, using CAD (Computer-Aided Design), and creating 3D models to picture and perfect their designs.
All in all, industrial design plays a really important role in shaping how everyday things look and work, making them better for people to use, and sparking new ideas in industries all over the globe.
How Does Industrial Design Start To Emerge?
1. Industrial design as we know it today began in the industrial revolution in Great Britain in the mid-18th century. This was characterized by industrial revolution where things that were previously painstakingly handcrafted gained mass production.
2. Shift in Manufacturing:
Product design became an important role since productions were being done by machines and products that were to be produced had to be produced on a large scale.
3. Rise of Consumers:
The growth of industry and rising consumerism called for wonderful yet more cost effective and fashionably designed products.
4. Global Trade:
Colonialism entailed high foodstuffs acceptance and more diversified markets which required diverse product designs.
5. These factors stimulated the demand in industrial design but it was not acknowledged as an acceptable profession until early 19 century.
6. Peter Behrens:
Behrens is considered to be the first industrial designer because he applied design for the production of simple things for apartments in companies such as AEG (German- Allgemeine Elektricitäts-Gesellschaft) (English translation- General Electricity Company).
7. Arts and Crafts Movement:
The early industrial designers were influenced by the arts and Crafts movement with the people like William Morris wanting to propel the creation and use of high-quality objects with artistic value.
8. Bauhaus:
This German art school (1919-1933) played a key role in promoting the idea that craft, art and technology should unite and put a strong emphasis on functionality and minimalism.
9. These early pioneers laid the foundation for what industrial design is today: a field which incorporates parts of art, engineering, as well as product usefulness to create attractive and more useful products.
Industrial Design Evolution

1. Industrial Revolution (18th Century):
Creation of mass production. Functional, efficient, and standardized: Strategies in the redesigning of work. Consider cars and factory assembly lines for furniture and their primitive tools.
2. Arts and Crafts Movement (19th Century):
A statement of the demise of the product with mass production. Focus on product simplicity and quality. Encouraged industrial designers to take looks into account while designing products.
3. Bauhaus and Modernism (Early 20th Century):
The Bauhaus movement that existed in Weimar Germany promoted the idea of uniting art with the technology. This led to styles that are simple yet elegant and prioritized functions. Picture the straight lines, the sharp angles, pieces of furniture in a post that says “form follows function,” and so on.
4. Streamlining and Art Deco (Mid-20th Century):
Began incorporating designs to consumer products that reflected speed and technology. Art Deco employed geometric shapes and used luxurious elements and exuded glamour. Art Deco also included new invention such as electricity using lighting and geometric shapes.This rise saw great designs in everything from cars and furniture to toaster and radios.
5. Post-War Boom and Pop Culture (Mid-20th Century):
The Second World War brought a boost to the industrial design as factories that were making war weapons changed the focus to products for the people. This period prioritized the focus on the users and also welcomed new materials such as plastics. The modernization of the society and planned obsolescence were the key design trends.
6. User-centered Design (Late 20th Century – Present):
Environment issues resulted in placing emphasis on the use of sustainable materials and energy efficiencies. The user experience gained significance as products were crafted in such a way that they were easily used. Innovation like the introduction of the computer and digital modeling changed the design significantly.
7. Technological advancements (Late 20th Century – Present):
Computers and digital modeling introduced new opportunities in designing products making it more creative and effective. 3D printing technology has revolutionized the aspect of fast prototyping and complex shapes designing.
8. Sustainable design (Late 20th Century – Present):
The environmental awareness required the use of sustainable materials and energy conservation. Today’s designers focus on the product lifecycle from its manufacturing to its disposal.
9. Integration of technology (Present – Future):
Sustainability and ethical manufacturing will be the continued focus in the coming times.Integration of advanced technologies such as 3D printing and artificial intelligence will additionally shape industrial design. A focus on seamless user experiences for physical and digital products.
10. Design thinking and innovation (Present – Future):
Design thinking is a human-centered approach to complex problem-solving in industrial design. This methodology enables designers to create products that are innovative and answer user needs.
4 Types of Industrial Design
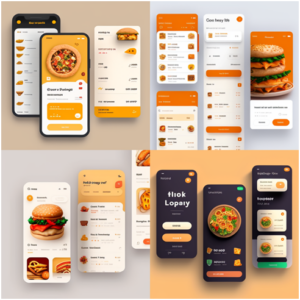
1. Product Design
Evolution-
Product design has undergone transformation in its own right since the beginning of time and is influenced by various factors like technology, social trends, and user needs. The era of pure functionality in the Industrial Revolution gradually shifted into user-centeredness and sustainable approaches in today’s world. See previous response for detailed evolution points.
Define
Product Design is a process of ideating, making, and improving products that solve problems for the users. It encompasses the entire cycle in which a product would finally go to production and usage.
Use
Product design finds its application in most industries in designing a wide array of products:
Physical products
furniture, appliances, electronics, clothing, tools, toys, medical equipment, etc.
Digital Products
Websites, mobile apps, software interfaces, and user experience for digital platforms.
Services
Designing the user experience for a service like how a customer interacts with a bank or interacts with a ride-sharing application.
Application
Product design rules can be used for anything people use.
User Research: Find out what users need and how they act by using surveys, interviews, and tests.
Ideas & Sketching: Think of new ideas; draw and make models.
Usability Tests: See how users use the product. Find and fix issues.
Looks & Function: Make it look good and work well.
Materials & Making: Pick the right stuff and ways to make for the product and users.
By using these ideas, product makers craft tools that work well and boost user joy. This leads to the product’s user experience and contributes to the overall success.
Famous Product Designers
Jonathan Ive

Karim Rashid

James Dyson

Zaha Hadid

Frank Lloyd Wright

Achille Castiglioni

Naoto Fukasawa

Dieter Rams

Philippe Starck

Marc Newson

Top Product Design Companies in India
Tata Elxsi
Infosys

Wipro

HCL Technologies

Mindtree

Accenture

IBM India

Career Options in Product Design
i. Career building:
- Education and Skill Development: education in industrial design, product design, or a related field and key skills such as sketching, 3D modeling.
- Portfolio and Experience: strong portfolio and experience through internships, freelance work
- Networking and Industry Engagement:Connect with professionals in the field through online platforms and Seek mentorship
- Specialization and Continuous Learning:Consider specializing in area of product design such as sustainable design, UX design
ii. Opportunities
- Product Manager
- Product Marketer
- Industrial Designer
- Design Consultant
- Design manager/ Director
- Product manufacturers
- UX/UI Designer
- Service Designer
- Brand strategist
- Packaging designer
- Design educator/ professor
- Freelance designer/consultant
Top India’s Best Colleges for Product Design

National Institute of Design (NID): Bachelor of Design (B. Des.) in Product Design, Master of Design (M. Des.) in Product Design

UID (United World Institute of Design): Bachelor of Design (B. Des.) in Product Design, Master of Design (M. Des.) in Product Design

MIT Institute of Design: Bachelor of Design (B. Des.) in Product Design, Master of Design (M. Des.) in Product Design

Industrial Design Centre (IDC), IIT Bombay: Master of Design (M. Des.) in Product Design, Master of Design (M. Des.) in Mobility and Vehicle Design
Indian Institute of Technology (IIT): Bachelor of Technology (B.Tech.) in Product Design, Master of Design (M. Des.) in Product Design
Works of Product Designers
Product Rendering of Aqsa Areebah (Artans Batch2022-2023)


Prototyping

Product Sketching (Digital)

Product Sketching

Design Thinking

2. Transportation Design
i. Evolution
Transportation design has changed over time. Early designs focused on function. Today’s designs focus on safety, green tech, and user comfort. The Industrial Revolution brought big shifts. The mid-1900s saw sleek looks. The post-war boom was all about user experience. Now, electric and self-driving cars are shaping the future.
ii. Define
Transportation layout is the manner of designing motors, infrastructure, and transportation structures. It considers aesthetics, usability, ergonomics, protection, and environmental effect to create person-friendly, green, and sustainable transportation solutions.
iii. Use
Transportation design is used to create an extensive type of motors and systems for:
Personal transportation: Cars, bikes, bicycles, scooters, and so on.
Public transportation: Buses, trains, trams, subways, and so on.
Air travel: Airplanes, helicopters, and so forth.
Water travel: Ships, boats, ferries, and many others.
Micro mobility: E-scooters, e-bikes, and so on.
Shared mobility services: Car-sharing, motorbike-sharing, etc.
Infrastructure: Train stations, bus stops, airports, roads, and so on.
iv. Application
Transportation designers practice their capabilities in diverse methods:
Exterior Design: Shaping the general appearance and experience of a automobile or infrastructure.
Interior Design: Creating snug, functional, and user-pleasant interiors.
User Interface (UI) Design: Designing interfaces for facts systems in vehicles (e.g., dashboards).
User Experience (UX) Design: Crafting a unbroken and enjoyable user revel in all through a transportation adventure.
Ergonomics: Designing seats, controls, and layouts which might be comfortable and safe for users.
Sustainability: Choosing substances, designing for strength efficiency, and considering the lifecycle of an automobile.
Transportation layout is a continuously evolving area that performs a crucial position in shaping the destiny of mobility.
Famous Transportation designers
Giorgetto Giugiaro

Batista Pininfarina

Marcello Gandini

Ian Callum

Walter De Silva

Peter Stevens

Chris Bangle

Peter Schreyer

Shiro Nakamura

Henrik Fisker

Top Transportation Design Companies in India
Maruti Suzuki
![]()
Hyundai

Tata Motors

Mahindra

Honda

Skoda

Volkswagen

Renault

Career Options in Transportation Design
Career building
1. Get the basics down: Get really good at sketching, using 3D modeling software, and understanding industrial design principles.
2. Dive into the nitty-gritty of transportation: Learn about vehicle engineering, ergonomics, and designing for people’s mobility needs.
3. Keep up with the latest: Stay in the loop with new technologies like electric vehicles, self-driving cars, and eco-friendly materials.
4. Think about formal education: Think about doing a bachelor’s degree in transportation design, industrial design, or automotive design.
5. Show off your work: Build a strong portfolio that highlights your design skills, creativity, and understanding of transportation requirements.
6. Connect with people: Go to industry events, get involved in online communities, and find a mentor.
7. Stay passionate and keep those creative juices flowing: Stay inspired, think about the entire user experience, and never stop learning.
Opportunities –
Automobile Exterior Designer,
Interior Designer,
Ergonomics Lead,
CMF Designer, Design Manager,
Business Development,
Accessory Designer,
UX Designer
Top India’s Best Colleges for Transportation Design
National Institute of Design (NID)

UID (United Institute of Design)

MIT Institute of Design

IIT Bombay

Works
- Design and consumer research
- Color and trim
- Concept development sketching
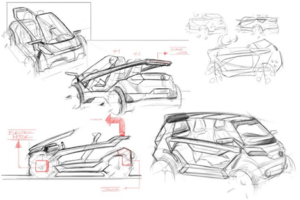
CAS (Computer Aided Styling)
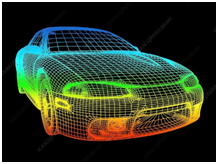

Clay modeling

Interior buck model

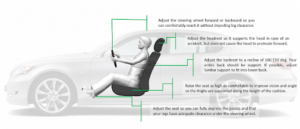
Vehicle ergonomics
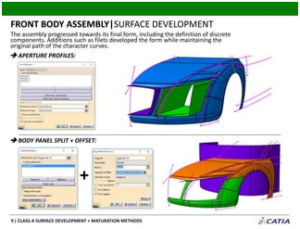
Class-A Surface Development
3. Packaging Design
i. Evolution
Packaging design has come a long way, going beyond just being functional and turning into a strategic marketing tool. It all started with using materials like leaves and animal skins to protect stuff. Then came the Industrial Revolution, which brought us faster and cheaper ways to package things. As branding and marketing took off, packaging became even more important. In the mid-20th century, technological advancements gave rise to cool and eye-catching packaging designs. And now, sustainability and digital marketing are making their mark on packaging design, shaping its future.
ii. Define
Packaging design is all about the art and science of creating the perfect container or wrapper for a product. It’s not just about making it look good, though. This field takes into account things like functionality, brand identity, user experience, and even the impact on the environment. The goal is to create packaging that not only protects and informs, but also sells the product. It’s a delicate balance, but when done right, it can make a huge difference.
iii. Use
Packaging design is crucial for a whole bunch of different products:
- Food and drinks,
- Cosmetics and personal care items,
- medications and medical supplies,
- Electronics and appliances,
- Clothing and fabrics,
- Even toys and games
- Durable goods
iv. Application
Packaging designers use their skills in different ways to create packaging that not only looks good but also works well:
1. Structural Design: They come up with the physical form and functionality of the packaging, like boxes, bottles, and pouches.
2. Graphic Design: They design the visual elements of the packaging, such as logos, colors, fonts, and images.
3. Branding: They make sure that the packaging design matches the overall brand identity and message.
4. User Experience (UX) Design: They focus on making the packaging easy to open, close, and dispose of.
5. Sustainability: They choose environmentally friendly materials and design packaging that can be recycled or biodegraded.
6. Marketing and Information: They use the packaging to communicate product details, the brand’s story, and marketing messages.
These different aspects together make sure that the packaging not only looks great but also serves its purpose effectively.
Famous Packaging Designers
Paula Scher

Karim Rashid

Emily Perkins

Landor Associates

Bruce Nussbaum

Top Packaging Design companies in India
Elephant Design

What a Story

Confetti Design Studio

Designer People

Buttercup Advertising Studio

Career options in Packaging Design
Career Building in Packaging Design
Skills & Education:
Graphic design, illustration, and software skills.
Formal Education – Graphic Design, Industrial Design or Packaging Design programs.
Portfolio demonstrating design abilities and packaging knowledge.
Experience & Network:
Internships or entry-level experience.
Network – attend packaging events, join design organizations, and connect online.
Specialize:
Sustainable, luxury, food & beverage packaging among others.
Stay Relevant:
Workshops, industry publications, trends, and sustainability.
Opportunities –
Sustainable Packaging
E-commerce Packaging
Smart Packaging
Subscription Boxes
Global Packaging Design
Experience-Driven Design
Top India’s best colleges for Packaging Design
There are no specific colleges for Packaging design they are included in Industrial design subjects.
Works
Packaging Designers conceptualize, research, design, prototype, aesthetically and coordinate with cross functional teams. They must think about sustainability, market insights and user experience whilst considering safety regulations and labeling requirements for the final product. Cost factors and sustainability through the product life cycle also play an important role.


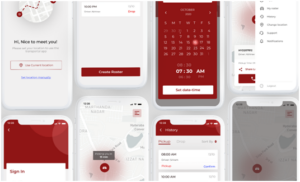
4. UX /UI Design
1. Evolution
The evolution of UX and UI design has come a long way. Initially, the main focus was on making products usable with consideration of keyboard shortcuts. With the advent of the web and the mobile revolution, designers started using Graphical User Interfaces, UX design principles, and user-centered design approaches.
In the future, we’ll see even more hybrid technologies that will integrate into the everyday life of users and offer personalized experiences. Voice recognition, augmented reality, virtual reality, and artificial intelligence are just some examples of advanced technologies that will influence the future of UX and UI design.
2. Define
User Experience (UX) Design: The design of products (digital or physical) that are easy, enjoyable, and efficient to use. This includes the whole user journey, from product positioning to actual use, covering aspects such as usability, accessibility, information architecture, emotion, and brand perception.
User Interface (UI) Design: The visual interface of a product. This involves the appearance and behavior of the different elements while a user interacts with the product. Layout, typography, color, iconography, and animation are all part of UI. It should be beautiful, intuitive and UX-friendly.
3. Use
UX/UI design can be applied to many different products and experiences. Here are some examples:
Websites and web applications
Mobile apps
Software applications
Desktop interfaces
Self-service kiosks
AR/VR experiences
Wearable technology
In-car entertainment systems
Any product with a user interface
Application
User research
Information Architecture
Interaction design
Visual design
Prototyping
Usability
testing
Accessibility
Famous UX/UI designers
Don Norman

Luke Wroblewski

Jakob Nielsen

Whitney Hess

Aarron Walter

Top UI/UX Design companies in India
Wipro

Infosys

AllianceTek

Accenture

UST Global

Fjord (Accenture Interactive)

Career options in UI/UX design
career building-
- Establish a Base: Think of earning a degree in design or taking online certification to master the basic principles of UI/UX design along with software skills and learning user research techniques.
- Acquire Key Skills: Visual communication, typography, layout designs, interaction design, and user research are some of the crucial skills needed for a UI/UX designer.
- Create a Portfolio: If you are designing a website a mobile app or a UI for a hypothetical product of your own, you go ahead and create a portfolio.
- Internship and Networking: Take up internships in web design firms, technology product companies or UX consulting companies to gain experience.
- Actively Network: Attend design events, meet UI/UX designers, and join design professional groups and networks like (AIGA, IXDA, and UIAA).
- Keep Yourself Updated and Continue to Learn: Enroll in workshops, attend conferences, and take online certification to enhance your knowledge about the latest trends, technologies, and design practices.
- Launch your career with an entry-level position in design firms or product companies and learn from experts while working on real projects.
Opportunities –
UX Researcher
UX Writer
UX Content Strategist
UI Designer
Conversational UI/UX Designer
VR/AR UI/UX Designer
Accessibility Specialist
E-commerce UI/UX Designer
Fintech UI/UX Designer
Top India’s Best Colleges for UX/UI Design
National Institute of Design (NID)

UID (United World Institute of Design)

MIT Institute of Design

Types of Industrial Design

Works
Understanding the User and the Product
Collaboration and Communication
Additional Responsibilities
Designing the User Experience (UX)
Creating the User Interface (UI)