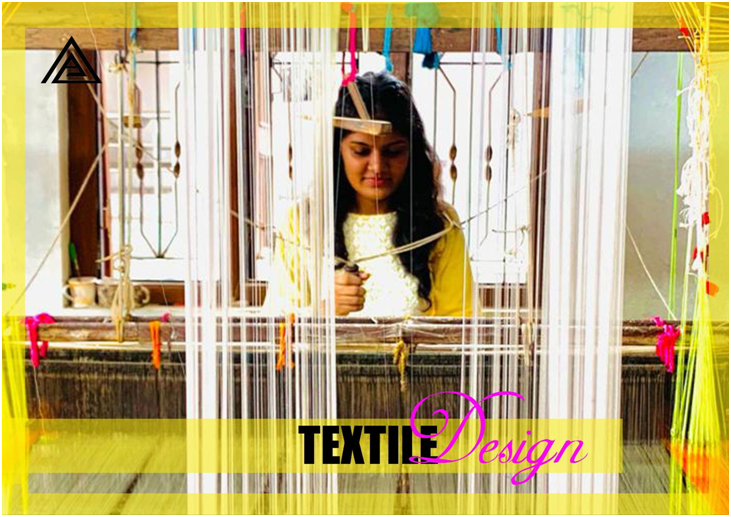
TEXTILES:-
The term textiles refer to the use of yarn, fibers, thread to create fabric. As technologies are progressing so textile based products are.

TEXTILE DESIGN:-
Textile design is a creative cum technical process of developing fiber into fabric with knowledge of material functionality.
For example:
1. Making of silk yarn to silk fabric

2. Making of wool to woolen sweaters

USE OF TEXTILE DESIGN:-
1. Clothing (e.g., shirts, dresses, pants, skirts, sarees, kurta and other wearables)

2. Home textiles (e.g., towels, drapes, curtains, bedsheet, pillow covers, cushions, footmates, placemats, laundry bags and more )

3. Interior décor (e.g., carpets, rugs and the same as above)

4. Functional purposes (e.g., sound control systems, Raincoat, Windcheaters etc.)

APPLICATION OF TEXTILES:-
1. TRANSPORTATION TEXTILES:-
Transportation textiles are the fabric used in various modes of transportation like buses, trains, airplanes, aircrafts etc.
Examples: Automobile Upholstery, Aircraft Interiors, Train Seating, Marine Upholstery, Automotive Carpeting, Airbag Fabrics, Seatbelt Webbing, Headliner Fabric, Luggage and Bag Materials etc.

Properties: flame-retardant and lightweight, easy to clean, resistant to wear and tear, stain resistant.
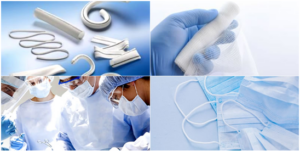
2. MEDICAL TEXTILE:
Medical textiles are the fabric and material used for healthcare purposes.
Examples: Surgical Gowns and Drapes, Sterile Wraps, Wound Dressings, Compression Garments, Medical Implants, Surgical Sutures, Disposable Medical Fabrics, Orthopedic Braces and Supports, Antimicrobial Fabrics, Drug Delivery Systems etc.
Properties: Provide a barrier against fluids and bacteria, Hypoallergenic, Antimicrobial, Breathability, Anti- bacterial, Sterility etc.
3. Industrial Products and Components:
used in manufacturing processes, machinery, equipment, and infrastructure related to textiles and textile production.
Examples: Filters in machine, Packaging material, Food storage etc.
Properties: Electrical Conductivity or Insulation, Breathability and Moisture Management, Dimensional Stability, Water Resistance and Waterproofing, Strength and Durability, Heat Resistance, Chemical Resistance etc.

4. Agriculture, Horticulture and Fishing:
textiles are utilized in agriculture, horticulture, and fishing to improve efficiency, protect crops and livestock, and sustainably manage natural resources.
Examples:
1. Agricultural Textiles:
- Crop Covers
- Mulching Fabrics
- Shade Nets.
- Fruit and Vegetable Bags
- Root Control Bags

2. Horticultural Textiles:
- Greenhouse Fabrics
- Shade Cloth
- Plant Ties and Supports
- Garden Fabrics

3. Fishing Textiles:
- Nets
- Ropes and Twines
- Aquaculture Nets
- Fish Harvesting Equipment

Properties: Mesh Size and Configuration, Flexibility and Elasticity, Biodegradability and Environmental Impact, Chemical Resistance, Temperature Regulation etc.
5. Home Textiles:
Textiles and fabric used in homes, offices, and residential areas for comfort and decorative purposes.
Examples:
1. Bedding and Linens:
- Sheets
- Pillowcases
- Duvet Covers
- Blankets and Throws

2. Towels and Bath Linens:
- Bath Towels
- Hand Towels Bath Mats

3. Curtains and Drapes:
- Curtains
- Drapes

4. Table Linens:
- Tablecloths
- Napkins
- Placemats

5. Kitchen Textiles:
- Dish Towels
- Aprons
- Oven Mitts and Pot Holders

6. Decorative Pillows and Cushions:
- Throw Pillows
- Floor Cushions

Properties: Durability and Longevity, Absorbency, Breathability, Colorfastness, Stain Resistance, Wrinkle Resistance, Easy Care, Thermal Insulation, Noise Reduction, Allergen Resistance, Decorative Appeal etc.
6. Clothing Components:
Clothing components are the textile and fabric material used in making and assembling a garment.
Examples:
Fabrics: cotton, polyester, silk, wool, denim, and spandex.

i. Trims and Embellishments:
- Ribbons and TapesLace
- Buttons and Fasteners
- Patches and Appliqués
- Braids and Cords

ii. Interfacing and Stabilizers: Used to stable fabric like in collars and cuff

iii. Linings and Underlinings

iv. Elastic and Stretch Materials

v. Labels and Tags

vi. Padding and Filling Materials

7. Packaging and Containment:
These textiles are used for protecting, packaging of materials, storage and more.
Examples: Food packaging, storage, non woven bags, Insulated packaging,Tarpaulins etc.
Properties: Strength and Durability, Flexibility, Barrier Properties, Water Resistance, UV Resistance, Chemical Resistance, Thermal Insulation, Breathability, Antistatic Properties, Environmental Sustainability etc.


8. Construction – Building and Roofing:
Construction textiles used in building and roofing processes for insulation, protection, reinforcement, and aesthetics.
Examples: Building Wraps:Roofing Membranes, Insulation Textiles, Reinforcement Fabric, Tarpaulins, Scaffolding Nets and Tarps, Soundproofing Textiles, Decorative Fabrics etc.
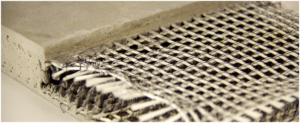
Properties:Strength: Weather Resistance, Waterproofing, Breathability, Flexibility, Chemical Resistance, Fire Resistance, Insulation, Lightweight, UV Stability, Abrasion Resistance etc.

9. Geotextiles in Civil Engineering:
Geotextiles are fabrics used in soil stabilization, drainage, erosion control, and construction of roads, railways, embankments, and retaining walls.

Properties: Separation, Filtration, Drainage, Reinforcement, Erosion Control, Protection

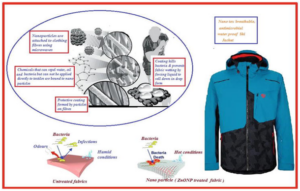
10. Sport and Leisure:
Sport and leisure textile has a wide range of fabrics and materials categories for various activities, from athletic performance to outdoor recreation and relaxation.
Examples: Athletic Apparel, Footwear Materials, Outdoor Gear, Swimwear, Leisurewear, Sports Accessories, Yoga and Fitness Gear, Team Sports Uniforms, Golf Apparel etc.

Properties: Moisture Management, Breathability, Flexibility and Stretch, Durability, Lightweight, Thermal Regulation, UV Protection, Abrasion Resistance, Compression, Antimicrobial and Odor Control, Quick-Drying etc.
METHODS USE FOR MAKING TEXTILES:
The textile manufacturing process follows various construction methods. Each method change the properties and functionality of the material. Below are a few examples:
1. Weaving:
Weaving is the oldest method followed for making fabric. In which the interlacing of two yarns or threads called Warp [Vertical] and Weft[Horizontal] on a loom.
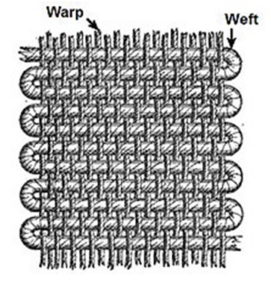
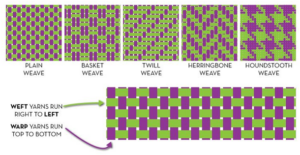
2. Different weaving patterns are:
Plain weave, twill weave, satin weave, herringbone, Double weave, houndstooth, basket weave, etc.
Rather than all the basic weaving techniques there is a technique used to create intricate pattern fabric by using Jacquard loom known as Jacquard weave.

3. Different types of loom:
Loom is a tool used for weaving helps in the interlacing of yarn. Below is some examples of looms, each following different characteristics:
i. Frame loom:
Used for small scale weaving. Also, you can achieve basic weaving patterns and create some tapestry patterns.

ii. Jacquard loom:
The speciality of jacquard is the card which you can see in the below image helps in creating the intricate or required pattern. Which you cannot achieve in frame loom.
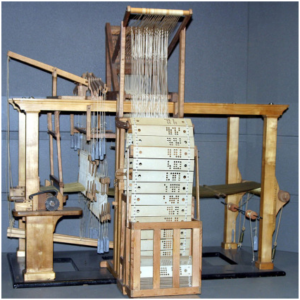
iii. Pit Loom:
This loom is set in ground for what is also known as Ground loom. For handling of the pit loom the weaver sits or stands above the loom. The creation of wider fabrics in Pit loom are traditional hand woven fabrics.

2. Knitting:
Knitting is the method of interlocking of loop yarn by using knitting needles or knitting machines to create textiles.

The fabrics made out of the knitting are stretchable which make it breathable, durable and different surface construction come up with different designs. Also, for it’s versatile functional applications knitted fabric used in fashion, sportswear, activewear, home textiles, and more.

Different types of stitching or looping in knitting: Knit Stitch, Purl Stitch, Stockinette Stitch, Garter Stitch, Ribbing, Seed Stitch, Cable Stitch, Lace Stitch etc.



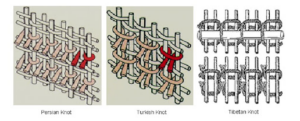
3. Knotting:
Knotting used to create some decorative items also an entire piece of fabric too. Knotting follows different techniques of knots:
Macrame: It is a textile crafting technique in which ropes and cords are used for making decorative items. Which you have usually seen in many households.

Knotting in Rug Making:
Different types of knot used to create carpet and rugs. As much as the count of knots makes the carpet more luxurious and expensive.

4. Condensing and pressing:
In these techniques yarn or fibers are heated and pressed which help in binding the fiber together without any interlacing or interlocking. Which creates compact fabric. For example: Felt

5. Crochet:
Crochet fabric created by interlocking of loop yarn by using crochet needle. It is similar to knitting but in crochet a single needle get used.

Products created from crochet: It is a versatile craft used to create garments, toys and more.
1. Clothing:
- Sweaters
- Hats and Beanies
- Scarves and Shawls
- Dresses and Skirts

2. Accessories:
- Bags and Purses
- Headbands and Ear Warmers
- Gloves and Mittens

3. Home Decor:
- Blankets and Afghans
- Pillows and Cushions
- Rugs and Mats

4. Toys and Amigurumi:
- Stuffed Animals
- Dolls and Doll Clothes

Difference between Crochet and knitting:

SURFACE EMBELLISHMENT ON TEXTILES:
Surface embellishment techniques take place on the surfaces of textile which make fabric decorative, creative and aesthetic.
1. Embroidery:
It is a surface decorative craft which is created by using thread and needle. For tightening the fabric either embroidery ring or Khat get used.

Different types of embroidery stitches:

Tools used for embroidery:

2. Printing:
It is a technique to apply color or design on fabric by using different methods of printing o make fabric decorative or aesthetic.
Printing methods:
i. Screen Printing: It involves a stencil screen of desired design through which color has been pressed by using squeezee. Which transfers the design on fabric. This is one of the oldest methods of printing.

ii. Rotary Printing: It is a high speed method of printing usually used in high production. This method involves rotation cylinders which have different colors of ink. The fabric passed through the rotational cylinders and color got pressed on the fabric which created the design.

iii. Digital Printing: Also known as inkjet printing. It involves digital technique of printing in which fabric gets through a special kind of inkjet printer which prints design on fabric. In digital printing we can get the desired design in output because there are no color limitations.

iv. Heat Transfer Printing: It involves heating and pressing in which design is printed on special transfer paper by using an inkjet laser printer. By applying heat and pressure the design transfers to fabric. This method is mainly used for custom t-shirts, bags and other personalized textile products.

The fabric used for these methods is mostly made out of synthetic fiber with heat-sensitive dyes.
v. Block Printing: It is a traditional method of printing, which involves the carving of wood to stamp on the fabric. For getting intricate design carved on 3-4 blocks which helps in detail design.


3. Surface Manipulation:
Textile surface manipulation is process of creating interesting visual or tactile effects on fabric surface by altering the surface texture, appearance, or structure.
Techniques:
i. Pleating: Fabric folds parallel or crease to create a pattern.

ii. Smocking: Fabric gathered and stitched together to create 3D patterns, textured, elasticized surface.

iii. Shirring: It involved gathering of fabric by using elastic thread in stitching in parallel rows.

iv. Quilting: It involves stitching of multi layer sandwiching of fabric. To create padded and texture effects. Mostly used in cushion covers, quilts, throws.

v. Pintucks: It involves small fold of fabric, stitched to create texture fabric surface. Mostly used in garment construction.

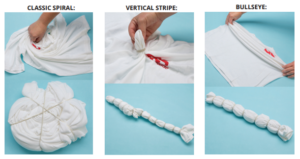
4. Tie and Dye:
It is a traditional technique of dyeing fabric. By tying the fabric with different techniques helps in creating a beautiful pattern.

Tying or Binding Techniques:
- Spiral
- Accordion
- Crinkle
- Shibori etc.
5. Tufting:
It involves the inserting or yarn into the fabric to create piles or textured surfaces. Used for making wall hanging, carpets, footmates done by hand or machine.

FAMOUS TEXTILE DESIGNERS:
India has a rich ancient history of textile from calling different crafts from each region, which make it popular world wide. Here are some famous textile designers who contribute their effort to spread and keep it alive.

Ritu kumar

Abraham & Thakore

Rohit Bal

Sabyasachi Mukherjee

Tarun Tahiliani

Anita Dongre

Gaurang Shah

Masaba Gupta
TOP TEXTILE COMPANIES IN INDIA:
1. Reliance Industries Limited

2. Arvind Limited

3. Welspun India Ltd

4. Raymond Group

5. Vardhman Textiles Ltd

6. Bombay Dyeing & Manufacturing Company Limited

CAREER OPTIONS IN TEXTILE DESIGN:

1. Career Building:
- Essential skills
- Knowledge of design principles and style.
- Innovation and creativity.
- Appreciation for art and fashion.
2. Opportunities:
- Vast-ranging career paths:
- Fashion industry.
- Home décor and furnishings.
- Textile manufacturing and production.
- Interior design and architecture.
- Retail and marketing.
- Medical Industry
- Agriculture
- Textile technician etc.
TOP 10 INDIA’S BEST COLLEGES FOR TEXTILE DESIGN:
Government:


NIFT NID
Private:






- Pearl Academy
- Symbiosis Institute of Design (SID), Pune
- Amity School of Fashion Technology, Noida
- Srishti Institute of Art, Design and Technology, Bangalore
- IIFA LANCASTER DEGREE COLLEGE, BANGLORE
- UNITEDWORLD INSTITUTE OF DESIGN [FOR MDES.]
OUR TEXTILE DESIGN STUDENT WORK:
1. Crochet Handmade designer laptop bag

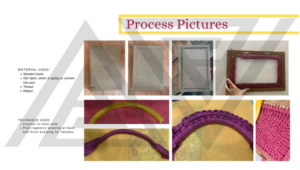



2. Student work: Embroidery
The Famous Artwork : Girl With Pearl Earring by Johannes Vermeer embroidered by using satin stitch.


3. Embroidery stitch exploration by our students:
i. Sequins and 3D flower embroidery

ii. Herringbone stitch with 3d elements:

iii. Ribbon embroidery on jute fabric:

iv. Leaf stitched on fabric by using blanket stitch:

For more info: www.artansarts.com
Contact: 9251110000,7009000266
Instagram: @nid_nift_uceed_nata_jeebarch